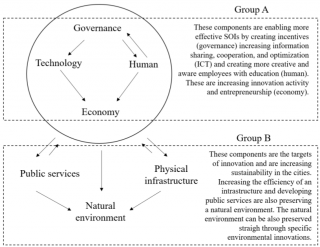
Elisa’s thesis entitled Smart City Approach as a Promoter of Sustainable Urban Development, included a wide literature review which then provided a framework of the components and indicators to assess the smartness of a city. Lappeenranta city was considered as a case example in the study. The development stage of the city was assessed as based on the publicly available material and secondary data, and future development suggestions for the city were provided.
The results of this research propose that by the increase of the intelligence of a city, the innovation activities and sustainable urban development can be promoted while also positively affecting to citizens’ perceived quality of life. To achieve all this, the interactive innovation platform is suggested to promote co-creation and engagement of different stakeholders (e.g., citizens and businesses) to work together for finding smart solutions for the common development issues.
Lappeenranta (www.lappeenranta.fi) is a good example of a city where the strategic goals, especially the environmental ones, well promote the growth of intelligence and development of smart solutions. Lappeenranta city strongly focuses on green development themes, and the city is committed to climate work. This is also seen in the recent achievements in practice, as Lappeenranta has won European Green Leaf 2021 title in a series of cities with less than 100,000 inhabitants. While the city is among the forerunners of green development, it makes it an interesting research object in the context of connection among smart and green city development approaches. Like many other cities in Finland, in terms of ICT skills, Lappeenranta is generally well equipped to promote smart urban development. More importantly, the city has also recently been active in introducing new methods to engage citizens for example in tackling with environmental issues, proposing new development ideas and in collaborative decision-making in participatory budgeting. All these new approaches support proceeding to the future pathways of collaborative innovation for smart sustainable urban development.
Elisa Rantala’s Master thesis is available HERE.
The thesis was supervised by Post-doctoral researcher Nina Tura and Professor Ville Ojanen from Lappeenranta-Lahti University of Technology (LUT University).