Today, satellite positioning (a.k.a GPS/GNSS) is a common service expected in all electronic devices (phones, watches, computers, etc.). And this need is expected to grow with the development of the Internet-of-Things (IoT) [1]. Over the last two decades, new GNSS constellations have appeared, for both military and commercial interests. Along with these constellations, new modernized signals came along. These signals are more complex but providing improved positioning for the modern usages of GNSS [2].
However, increasing the signal complexity comes with computational price. Acquiring and tracking these signals cannot be performed with legacy algorithms. Since the integration of these new signals, researchers have proposed countless new algorithms to improve measurements quality but also reduce their complexity, in order to reduce the energy consumption of receivers. Often, these two objectives cannot be achieved simultaneously, thus, highlighting the necessary trade-offs is required.
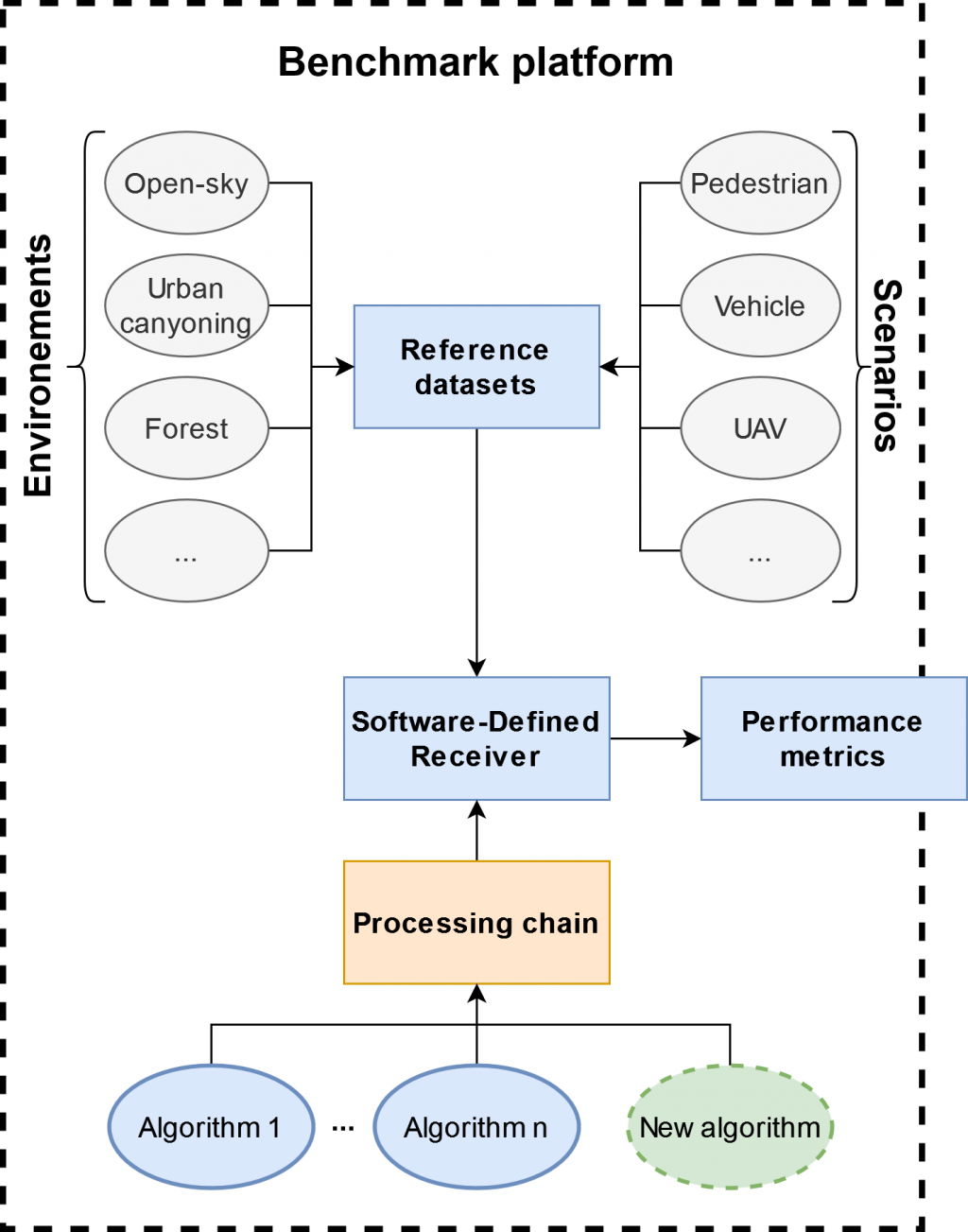
Yet, identifying if an algorithm is better than another is not straightforward, especially if they have been derived by different research teams. Their dataset and code will most certainly differ, and the comparison metrics might not be similar in the publication, depending on the team interest. Thus, unless the comparison is performed in a similar framework, it cannot be clearly assessed.
Our solution is to propose the development of an open-source research platform, to provide a common software and reference datasets. With these parameters, we maximize the comparability of algorithms to even allow benchmarking, while encouraging the dissemination of algorithms in open research.
The paper, available in the link below, presents the current development status of our tool and discuss the foreseen developments.
Link: https://zenodo.org/record/7347364
Proceeding’s version: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9943489
Acronyms:
IoT: Internet-of-Things
GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS: Global Positioning System
References:
[1] European GNSS Agency (GSA), “Power-Efficient Positioning for the Internet of Things,” 2020. White Paper.
[2] E. D. Kaplan and C. J. Hegarty, Understanding GPS, Principles and Applications. 3rd Edition. Artech House, 2017.

