Nowadays, technological advances perform a significant role in the healthcare systems development especially with the increased number of elderlies. eHealth systems’ importance is gained from the growing demands for medical care systems to observe several medical parameters. There is large diversity of required components of a wearable health monitoring and evaluation system such as biosensors, control units, wireless communication modules, processing units, medical shields, links, power supplies, wearable materials, advanced algorithms used for decision making and data extraction. In fact, the overall goal of a complex wearable healthcare system is to support design and development of the high impact personalized ICT healthcare services based on measurements of health state acquired by sensors capturing physical, cognitive and social activities. The acquired data will be fed into the risk prediction models or automatic evaluation modules to perform personal profiling and to identify deviations from the expected baseline of each specific user groups.
As an example, an eHealth system dedicated to Parkinson’s disease (PD) Patients Monitoring and Evaluation is emphasized. In the world there are 10 million people being affected by Parkinson’s disease which generally causes motor dysfunctions and affects quality of life [1]. Mostly, the patients motor disorders i.e., tremor, freezing of gait (FOG), bradykinesia, postural stability etc. are assessed by neurologists using traditional methods based on rating scales in clinical environment for a short span of time by performing some motor activities. The diagnosis based on this observation is doubtful and needs a thorough investigation. To fill this gap, we introduced A-WEAR bracelet [2]which supports clinicians in objective assessment of patients’ symptoms. However, there are still many aspects that need attention from researchers to enhance this eHealth platform in terms of small form factor wearable device with sensors which records all the important motor signals from both upper and lower limbs with wireless connectivity, better security and power efficiency.
With respect to medical point of view, it is crucial for medical practitioner to continuously monitor the patient’s movements when the severity of symptoms can be correctly identified, and the treatment can be judged. In order to benefit by fast real-time computing, avoiding component failure in the system, and providing high flexibility in receiving, storing and using data, a cloud-based solution is considered. Based on the aforementioned aspects, an eHealth architecture for PD patients as shown in the figure below is proposed. The patient will wear the A-WEAR bracelet which is enhanced with diverse sensors i.e., accelerometer, gyroscope and EMG sensors and insoles (printed with accelerometer and gyroscope sensors). After taking the specific medicine, the patient will perform some tailored exercises and some regular movements in clinic before observer so that the data is labelled. After some gap days, the same movements will be performed without taking the medicine and the data is labelled again by observer for severity estimation. During the gap days at home, the data is continuously recorded in home environment by bracelet and insoles and doctors can have access on the cloud platform.
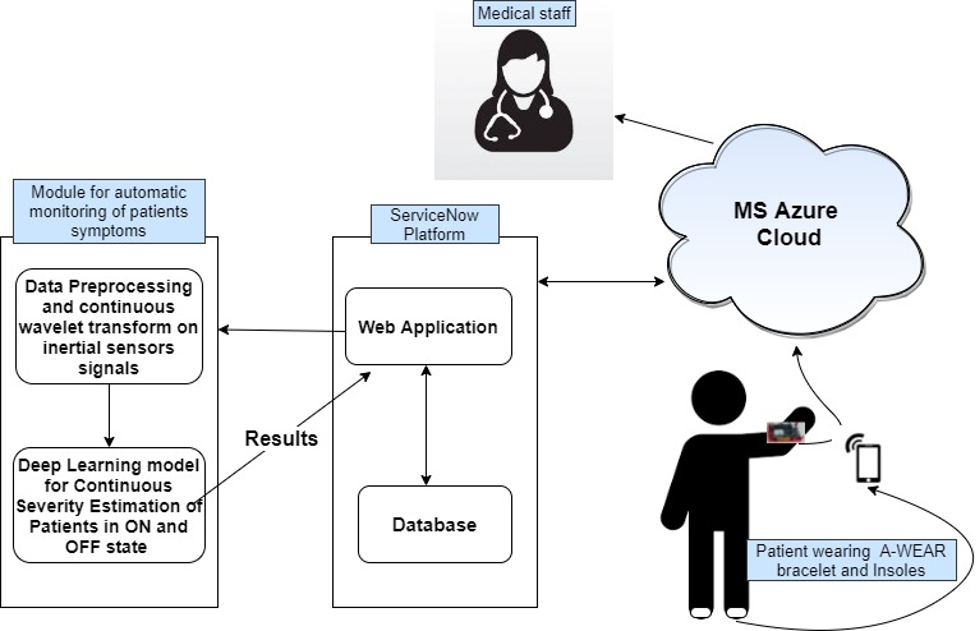
References